Spoofing attacks are when a hacker impersonates another authorized or trusted source on a network to launch attacks.
You can prevent spoofing network attacks by implementing spoofing detection software, enabling cryptographic network protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS), Secure Shell (SSH), and HTTP Secure (HTTPS), avoiding trusted relationships with unknown entities, and implementing packet filtering.
Learn More: How To Prevent Cyber Attacks
Free Security Policy Templates
Get a step ahead of your cybersecurity goals with our comprehensive templates.
What Is A Spoofing Attack?
A Spoofing attack is a means of falsifying any individual’s identity to gain unauthorized access.
As a result, attackers will cause internet activity to be rerouted and overburdened or redirected acquiring system access, data theft, and malware injection.
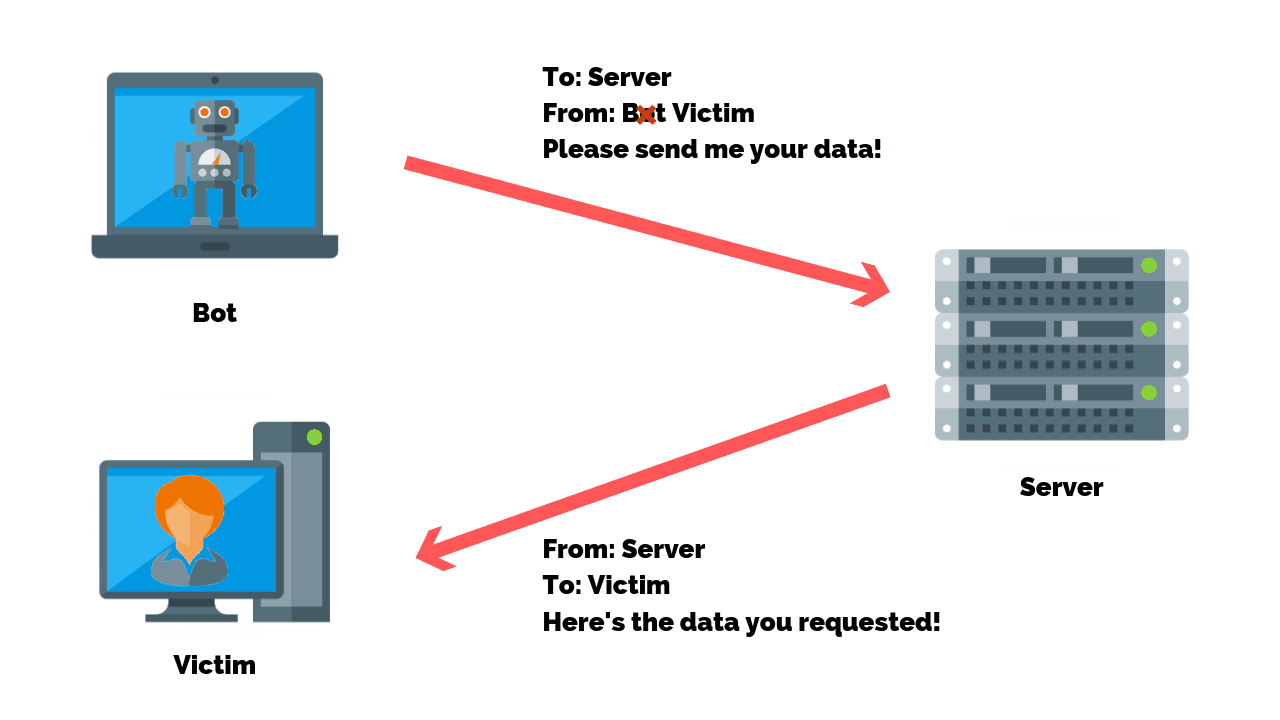
An advanced spoofing attack can steal your IP address, Domain System (DNS), Media Access Control Address (MAC), and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) while disguising itself as an authorized identity.
However, spoofing attacks are also prevalent through text message spoofing, email spoofing, URL spoofing, Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks, and caller ID spoofing.
Once initiated, spoofing attacks are difficult to spot and mitigate because they pay on deception and human error.
Why Are There So Many Spoofing Attacks?
Often, Spoofing is used for several malicious activities.
For example, an email posing as your CEO or coworker, asking you to resolve a work-related issue, prompting you to click on any link provided.
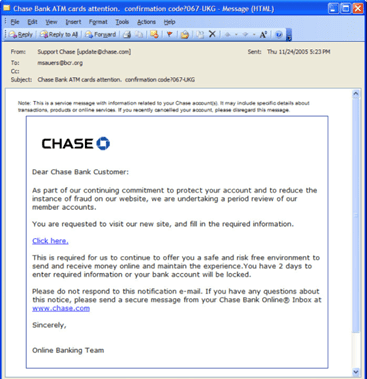
This link can lead you to disclose personal or financial information, send money, and download malware, which can lead to identity theft, fraud, and device damage.
At large, spoofing can cause data breaches and extreme financial burdens to an organization that is capable of completely crippling an infrastructure.
98% of cyber attacks contain one or more elements of social engineering like spoofing.
Example Of A Spoofing Attack
From 2013-2015 a Lithuanian man pretended to be an organization’s trusted vendor in Google and Facebook company supply chains.
The attacker spoofed business emails and created replica invoices of a Taiwanese technology manufacturer by the name of Quanta, then collected money transfers from these tech giants.
This Taiwanese company is known for building servers and other components for Google and Facebook so spotting the fraud was unachievable before being fleeced for over $120 million total.
This example of spoofing cost Facebook approximately $100 million and Google $23 million before catching on to the attack.
Evaldas Rimasauskas, a Lithuanian citizen, was only traced halfway across the globe due to the digital footprint he left behind.
Evaldas Rimasauskas was sentenced to five years in prison and reprimanded to pay over $90 million.
How Do You Prevent A Spoofing Attacks?
A few security actions you can take to prevent a spoofing attack include:
- Packet Filtering: Implement packet filtering to prevent IP address spoofing attacks. Packet filters block packets with incorrect source address information, making it harder for attackers to impersonate legitimate devices.
- Avoid Trust Relationships with Unknown Entities: Be cautious about relying solely on IP addresses for authentication. Trust relationships that exclusively use IP addresses can be exploited by attackers. Verify the legitimacy of devices through additional means.
- Deploy Spoofing Detection Software: Use specialized software designed to detect and prevent spoofing attacks. This includes monitoring for ARP spoofing, IP spoofing, and other deceptive techniques.
- Enable Cryptographic Network Protocols: Implement secure communication protocols to protect against spoofing. Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts data transmitted over networks while Secure Shell (SSH) Provides secure remote access to systems.
- HTTP Secure (HTTPS): Ensures secure communication between web clients and servers.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate your team about the risks of spoofing attacks. Train employees to recognize suspicious emails, links, and communication from unknown sources.
Article by