Vulnerability Management Best Practices
Learn what steps businesses need to take to burndown, remediate, and monitor vulnerabilities.
Learn what steps businesses need to take to burndown, remediate, and monitor vulnerabilities.
Author: Jason Firch, MBA / Last Updated: 02/17/23
Reviewed By: Josh Allen & Michael Swanagan, CISSP, CISA
View Our: Editorial Process
There are 8 vulnerability management best practices including Conduct Asset Discovery And Inventory, Classify Assets And Assign Tasks, Run Frequent Automated Vulnerability Scanning, Prioritize Vulnerabilities And Take Corrective Actions, Establish A Comprehensive Vulnerability Management Strategy, Use Automated Tools And Leverage Automation, Review Vulnerabilities And Generate Detailed Reports, and Integrate Vulnerability Management With Other Security Solutions And Processes.
In a world where hackers are lurking around every corner, we need to remain vigilant if we want to avoid becoming the next headline.
That’s where vulnerability management best practices come into play.
So, let’s start with the big question:
What are common methods for managing vulnerabilities?
To truly mitigate vulnerabilities, you need to have a multi-faceted approach that includes vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and patch management.
When it comes to vulnerability scanning, frequency, and visibility are key.
You should aim to scan your systems on a regular basis – we recommend at least weekly, if not more often.
In addition, you should prioritize vulnerabilities based on severity and remediate them in a timely manner.
Related Article: How To Reduce Your Mean Time To Remediate
Penetration testing is another crucial aspect of vulnerability management.
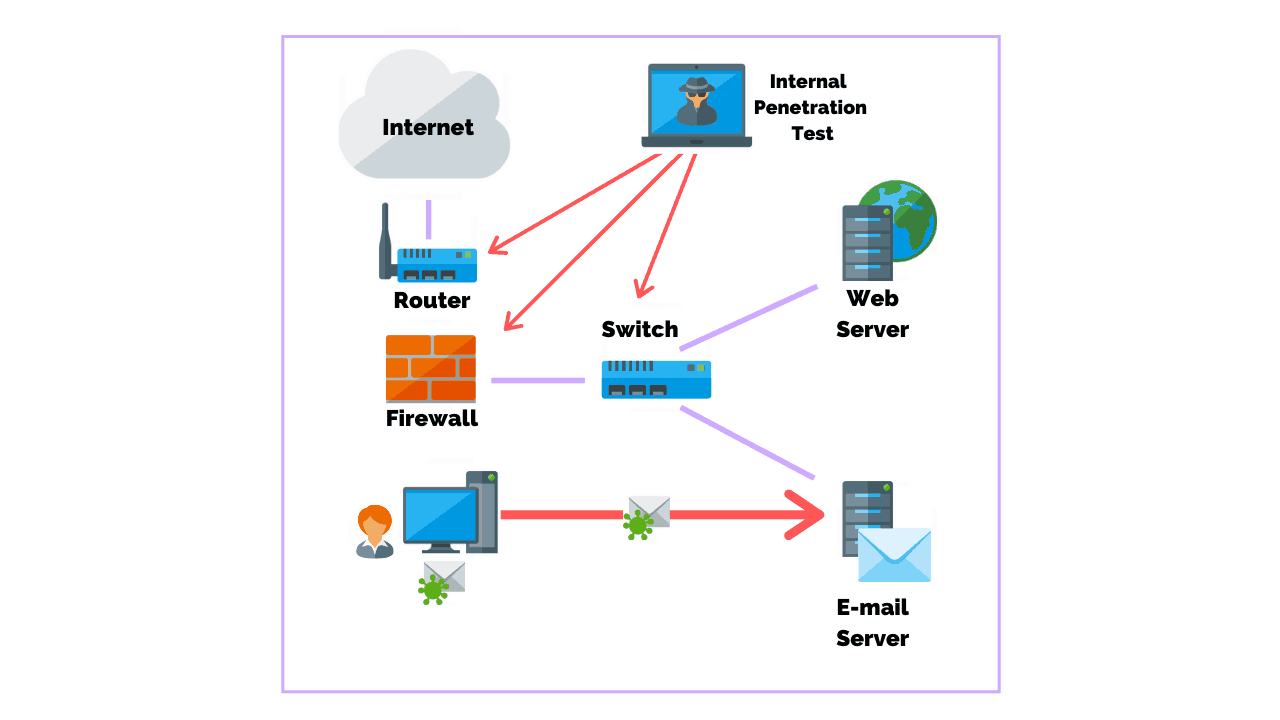
By simulating a real-world attack, you can identify vulnerabilities that may not have been caught by scanning alone.
We recommend conducting penetration tests on a regular basis, and always after major changes to your systems or software.
Enterprise patch management has been a contentious issue for decades, with conflicting opinions on how to balance earlier deployment and testing.
Patch management is tougher now due to dynamic and dispersed computing assets, as well as the sheer number of installed software components to patch.
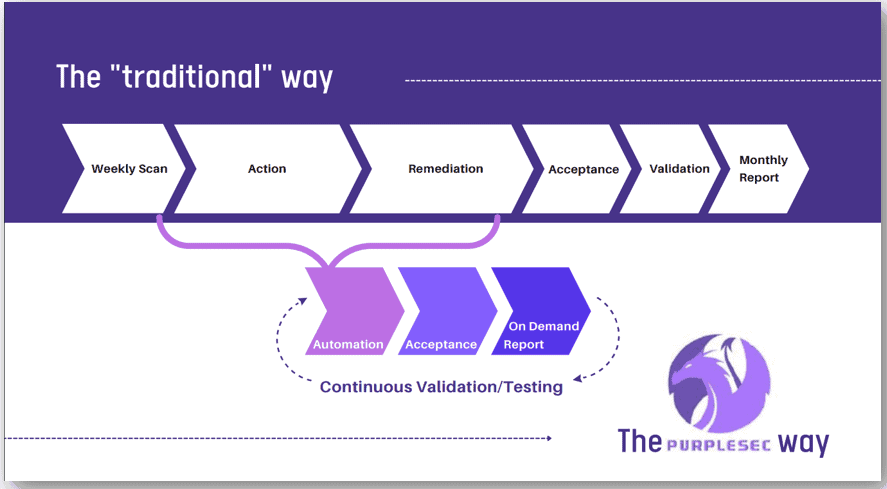
Many organizations are unable to keep up with patching, making it primarily reactive instead of proactive. Being proactive means doing more work now to reduce the likelihood of incidents in the future.
However, the disruptions from patching are largely controllable and necessary to avoid larger disruptions from incidents.
The recommendations in the NIST SP 800-40r4 supports principles of:
 The most important step in vulnerability management is to conduct a comprehensive inventory of all authorized and unauthorized devices on the network, including all software installed on the assets.
The most important step in vulnerability management is to conduct a comprehensive inventory of all authorized and unauthorized devices on the network, including all software installed on the assets.
This inventory should include devices and software owned and managed by the organization, as well as those owned by third-party vendors.
By having a complete inventory of all assets, organizations can determine which assets pose the most significant risk and prioritize vulnerability scanning accordingly.
Note: Asset based scans do not show the full picture. Instead, you should conduct a full IP discovery scan to ensure you have complete visibility of vulnerabilities.
After conducting an inventory of assets, it is essential to classify and rank them based on their true and inherent risk to the organization.
This risk classification will help determine the frequency of vulnerability scanning and the priority of remediation efforts.
It is also important to assign ownership of assets to system owners who are ultimately responsible for the asset’s associated risks and liability if those assets become compromised.
As part of continuous vulnerability management, organizations should run automated vulnerability scanning tools against all systems on the network on a frequent basis.
Vulnerability scanning tools should be:
Depending on the framework you follow the frequency of scanning should be at least every month or quarterly.
However, new vulnerabilities are found daily with many being weaponized by threat actors within days or hours after they’re discovered.
This means if you’re scanning monthly that your organization could be exposed to risk for the remaining 29 days in the month.
At PurpleSec, we recommend taking a continuous approach to your scanning. Depending on your organization weekly and perhaps daily scans may be appropriate.
After the scan is complete, organizations must prioritize vulnerabilities based on their impact on the organization and take corrective actions accordingly.
It is important to have a well-established process for remediating vulnerabilities, starting with high-risk vulnerabilities first.
When we say high risk we mean risk to the business and not CVSS scores.
To effectively manage vulnerabilities, organizations need to establish a vulnerability management strategy that includes people, processes, and technology (PPT).
The strategy should address the information needs of all stakeholders and reduce the organization’s risk.
It is important to plan ahead and establish KPIs to guide the security team and assess ROI.
When creating your KPIs we highly recommend focusing on these top ten to measure the success of you program:
Organizations should also understand and prepare for their elastic attack surface, which includes:
 Organizations should leverage automation to enhance the vulnerability management process.
Organizations should leverage automation to enhance the vulnerability management process.
Automated tools can help with:
By introducing automation into the vulnerability management process, organizations can reduce human error, cut costs, and save time.
After conducting vulnerability scanning and remediation efforts, organizations should review vulnerabilities identified in reports and prioritize remediation based on the risk rating.
It is also important to generate detailed reports for stakeholders to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
For example, by having visibility into vulnerabilities at a business unit level organization’s can quickly identify where bottlenecks exisit in remediating vulnerabilities.
They can then create a plan of action to address the issue or, in the case of legacy systems, accept the risk that patching those systems will take longer than others.
At PurpleSec, we believe that the argument of legacy systems “breaking” from installing patches is no longer valid in 2023.
Organizations need to look to reinvest in their infrastructure which may be posing a greater risk to reputation and financial loss.
Vulnerability management should be integrated with other security solutions and processes as part of a comprehensive solution.
Organizations should consider integrating vulnerability management with:
Integrating vulnerability management with other security solutions and processes provides a holistic approach to security, ultimately improving the organization’s security posture.
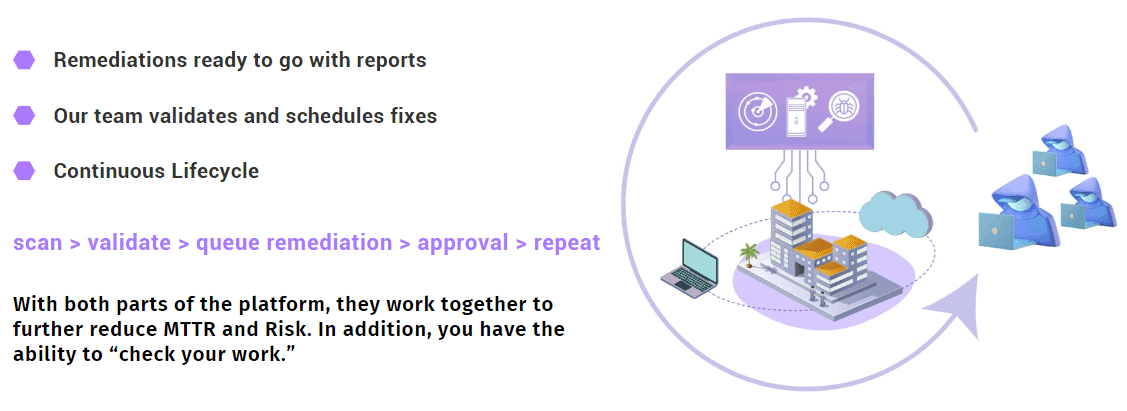
Likewise, results from penetration tests can be integrated into your vulnerability management process to quickly prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities identified.

Jason is a proven marketing leader, veteran IT operations manager, and cyber security enthusiast with 10 years of experience. He is the co-founder and CEO/CMO of PurpleSec.
Recent Articles
Categories
Policy Templates
Recent Articles:
Discover how to centralize your patch management effectively to enhance cybersecurity in your organization. Our guide explores the benefits, strategies, and tools for successful centralized patch management.

Discover how to scan for and fix Log4j vulnerabilities, ensuring the security of your Java applications while continuing to benefit from this widely-used logging library.

Discover shocking vulnerability management trends for 2023! Experts reveal predictions that’ll change the game – Stay ahead or be hacked!

Improve vulnerability visibility in networks & cloud environments with expert tips on strategies, KPIs, prioritization, & automation. Secure your assets now!

Discover best practices for Windows patch management! Learn how to streamline the process, overcome challenges, and reduce cyber attacks.

Struggling to bring your patch management up to speed? Learn the key challenges along with the solutions to tackle them head on.

Learn to effectively prioritize vulnerabilities in your organization’s cyber security efforts. Discover key factors, techniques, and examples for risk-based prioritization.

You can automate your patch management by selecting the right patch management tool that best suits your organization’s needs and configuring its automatic patching settings.
The main difference between vulnerability assessments and penetration testing is that vulnerability assessments identify potential weaknesses in an organization’s IT infrastructure through high-level security scans. Penetration testing goes a step further.

Credentialed scanning, using privileged credentials, provides in-depth vulnerability analysis and accurate results, assessing systems and apps not usually accessible without authentication. Uncredentialed scanning, without privileged credentials, is less accurate but can still reveal exploitable basic vulnerabilities.

Vulnerability scanning is a process of identifying and assessing security weaknesses in a computer system, network, or web application. Vulnerabilities can range from technical flaws in software, hardware or configuration issues to vulnerabilities in policies and procedures.
A vulnerability assessment is the process of identifying vulnerabilities and classifying risk in an infrastructure. The assessment also seeks to identify weaknesses in all connected systems to determine the most effective security measures.

Patch management refers to the process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and installing software updates (also known as patches) to an organization’s systems.
Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, prioritizing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and networks to reduce the risk of cyber attacks and protect against potential threats.
The top best practices for managing vulnerabilities in the cloud in 2023 include establishing KPIs, staying up to date with threat intelligence feeds, utilizing a vulnerability database repository, and leveraging automation, AI, and ML.

We help you identify and define the top key metrics that your organization can implement to track the progress and state of your vulnerability and patch management programs.

You can implement and enforce patch management policies by monitoring processes, configuring group policies, and using a patching tool such as SCCM, Satellite, or Wsus.

Next-generation vulnerability management activities provide continuous monitoring of an IT environment and automation to reduce the burden on IT security teams, reduce mean time to patch, and improves your return on security investment.

The vulnerability management lifecycle is a process intended for organizations to effectively identify, remediate, and confirm the elimination of network vulnerabilities in a computer system.

The main difference between patch management and vulnerability management is that patch management is the operational process of applying remediations (patches) to vulnerable systems.

Learn what vulnerability management is and how businesses can succeed in maturing their security posture by building a formal program.
Risk-based vulnerability management optimizes remediation activities based on the risks that each vulnerability poses to an organization.

What makes for a successful vulnerability management program and what common pitfalls should you avoid? Our security experts explain.

Automating vulnerability management eliminates repetitive tasks prone to human error and replaces them with data-driven vulnerability prioritization.
The average time to patch a critical vulnerability is reported to be 60 days. In this article, we identify a solution for how companies can reduce their mean time to patch vulnerabilities to dramatically reduce cyber risk.
With billions of dollars lost annually to threat actors, who continually gain access to an organization’s weak point, regulators and businesses are seeing the importance of addressing and repairing vulnerabilities.

If the report contains pages of vulnerabilities and is not clearly presented to your executive management team, it will be difficult to receive continued support for future investments.

While every business need is different, it’s best practice to perform network vulnerability scans at least once per quarter.
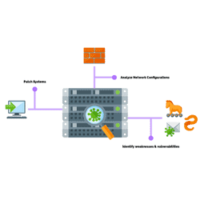
Vulnerability scanning identifies vulnerabilities within systems on a network. Penetration testing simulates an attack to exploit vulnerabilities.

A network vulnerability assessment is the process of identifying security vulnerabilities in systems, quantifying and analyzing them, and remediating.

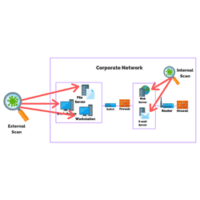
Internal vulnerability scans have access to an internal network or credentialed account, while external scans identify vulnerabilities from outside the network.