Why Vulnerability Management Reports Fail (& How To Fix It)
Learn about PurpleSec’s fully managed vulnerability management services.
Author: Michael Swanagan, CISSP, CISA, CISM / Last Updated: 10/14/2022
Reviewed By: Josh Allen & Rich Selvidge, CISSP
View Our: Editorial Process
Table Of Contents
You can fix your vulnerability management reporting by ensuring documentation is clear and concise, written with specific audiences in mind, is actionable, includes findings and metrics, establishes POA&Ms, and shows success and work completed.
What You’ll Learn
- Key elements that should be included in any vulnerability report.
- Understanding the difference between traditional reporting and risk-based reporting.
- Tips and tricks for reporting vulnerabilities to executive management.
- Common pitfalls to avoid when developing reports.
- How PurpleSec is improving the vulnerability reporting process.
Typical vulnerability assessment reports are designed for IT and security professionals to review.
This is not a problem since these teams support the tool and know the environment, however, presenting the same level of reporting to your leadership team generally does not convey the true value of your vulnerability management program.
If the report contains pages of vulnerabilities and is not clearly presented to your executive management team, it will be difficult to receive continued support for future investments.
Although your goal is to implement vulnerability best practices, this may eventually lead to burn out if your efforts are not realized.
If the report contains pages of vulnerabilities and is not clearly presented to your executive management team, it will be difficult to receive continued support for future investments.
Although your goal is to implement vulnerability best practices, this may eventually lead to burn out if your efforts are not realized.
In this article, we will discuss what vulnerability reporting should look like for your leadership team.
We will also explore how you can develop reporting with actionable insight using PurpleSec’s Vulnerability platform, which will enable you to develop effective reporting for your IT teams and executive management.
Let’s begin by examining the key elements that go into creating a successful vulnerability management report.
What Are The Key Elements Of A Successful Report?
In order for your vulnerability reporting to be successful you must include the following key elements:
Be Clear & Concise
The report should be free of data that does not clearly illustrate risk and the impact to business operations.
Precise information that targets risk related to key assets will provide the most value.
Concise reporting with illustrative graphs or charting is highly recommended.
Include an executive summary, usually one page which includes a high-level summary section and a few charts that visualize the key metrics scaled to a time period.
Know Your Audience
Prepare reporting with two audiences in mind:
- Technical Infrastructure Teams – Developers, Server Teams, Application owners. These teams need to know what and how to remediation specific vulnerabilities. This type of report is usually technical in format and provides guidance and recommendations on remediation efforts.
- Executives – Although some executives may have technical backgrounds, it is recommended to summarize the results with precise details illustrated with a few charts. Executives are looking to understand the impact and what the report is telling them about the business.
Make It Actionable
The goal of the report should do more than just provide a report with nice charts and pages of vulnerabilities.
There should be guidance on what to do next.
The remediation recommendations should be based or defined in your service level agreement as stated in your vulnerability management policy.
Include Findings & Metrics
The output of the report should clearly capture and illustrate remediation metrics.
The report should rank vulnerability findings per severity level – Critical, High, Medium, and Low.
Systems with the highest priority should be illustrated along with a risk metric.
This will help leadership understand the risk and impact to the business.
Establish A Plan Of Action And Milestones (POA&Ms)
It is critical to define the length of time a vulnerability should be remediated based on its severity level or priority.
Once this is understood and communicated to your infrastructure teams, plans of action and milestones would then be established.
Create a model that illustrates the number of vulnerabilities per severity level over time.
Demonstrating the trending is valuable and will help your audience understand the value of the risk metrics.
Tracking POA&Ms will help you make better strategic decisions for managing risk and demonstrate value to the executive leadership team.
Show Success & Work Completed
Once POA&Ms have been established and the infrastructure teams are provided with a path for resolving vulnerabilities, it is now time to show the work that has been done by the teams.
The final report should show the successes as well as the remaining open events.
This data can be used to illustrate the progress and maturity of the program over time.
Define Your Reporting Metrics Early
Incorporating and defining metrics early in the reporting process establishes a baseline for continuous reporting.
The metrics you define early for your organization can be used to demonstrate the value and benefits of the vulnerability program to your management and infrastructure teams.
In this section, we will examine key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help make your reporting successful, along with the top metrics your organization should be tracking.
The first step is to define your Service Level Agreement (SLA) within your vulnerability management policy.
Planning Vulnerability Timelines
Define an SLA. Establishing a timeline to remediate vulnerabilities provides clear direction on when vulnerabilities should be handled.
The remediation timeline should focus on severity levels and the value of the assets to the organization.
The SLA should be very specific on the remediation timelines.
For example, A zero-day attack timeline should be immediate, whereas a medium level vulnerability may have a timeline of up to 60 days to remediate.
This value is typically derived from the risk appetite of the business.
Top Vulnerabilities Metrics To Include In Your Reporting
- Mean Time To Patch (MTTP) – Average time it takes to patch a vulnerability. Generally calculated by subtracting the difference in time between the official release date of a patch and the time it takes to install the patch on the average of supported assets. The MTTP time should not exceed the number of days between the next maintenance period.
- Median Time to Respond/Remediate (MTTR) – Measurement of time elapsed between the occurrence of a security incident, time of discovery, when it was investigated, and contained.
- Median Time to Detect (MTTD) – The average length of time it takes a cyber security team to discover incidents within their environment.
Vulnerability Details To Include In Reports
- Vulnerability Name – This is generally a description of the vulnerability based on the scan engine or CVSS score and description.
- Severity – Vulnerabilities are weighted to provide a scale of criticality. In most cases, Severity levels are ranked 1 – 5, 5 is Critical, 4 is High, 3 medium, 2 Low, 1 is informational.
- Create Date – The create date is the starting point for the metrics – MTTD, MTTR, and MTTP.
- Organization’s Risk Rating – Based on current open vulnerabilities across your organization weighted by the business impact of the system. Establish SLAs based on if said vulnerability is not remediated within the established timeline. A breach of an SLA will present a higher risk to the organization.
Traditional Reporting VS Reporting Based On Risk
Traditional reporting provides a sum of all vulnerabilities based on severity level. A risk-based vulnerability management report is based on the calculation of risk factors.
Risk Factors
- Prioritization of the asset – how important it is to the business.
- Asset context – description and relevant attributes.
- Risk appetite – tolerance level for open vulnerabilities.
The report should also include exceptions or accepted risks that have been approved for non-remediation.
This information should be illustrated in a trending chart that depicts the current security posture compared to the results of the previous report.
Now let’s move on to the fun part.
We have the key metrics defined and the SLAs within the policy communicated to the appropriate teams, let’s now discuss how to present the report to your executive leadership team.
How To Report On Vulnerabilities To Management
As mentioned earlier in this article, one of the key steps in reporting vulnerabilities is to know the audience.
Understand that the role of executive leadership is to lead the business, not vulnerabilities.
So, the effectiveness of the reporting depends on how well the results are summarized and communicated.
Let’s review a sample of topics to include in the vulnerability management report:
Create An Executive Summary
This section should be concise and brief. Risk to the business is generally illustrated here within a chart and explained in non-technical terms.
Communicate your action items and next steps, with the goal of reducing risk in within your established timelines.
Report On Crown Jewels
Reporting on the systems that have the highest impact to the business are important to the management team.
Be sure to identify and prioritize the most critical assets and highlight the risk associated with these systems.
Communicate the risk impact if a critical system is breached and illustrate this measurement in a chart or metric. Communicate upcoming or future efforts to remediate issues and lower risk.
Create A Risk Metric
Each organization will be different on their approach and appetite for managing risk.
Identify your critical assets and create a custom risk classification or asset tagging if needed.
Set A Reporting Cadence
Set up a re-occurring meeting with your stakeholders to review the reports.
Meetings with infrastructure teams are generally held more frequently, with the goal of reducing MTTR.
Whereas management meetings are usually low in frequency, monthly or quarterly.
- Monthly Reports – These reports provide a breakdown summary of compliance and remediation statistics. These reports can be designed for a specific business unit and presented to the infrastructure team, project team members, or 3rd party vendors as required.
- Quarterly Reports – This meeting is typically higher level in nature and is geared for management teams. The purpose of the meeting is to present a high-level overview of the program that and reports the status of key milestones and objectives. This meeting usually includes leaders of the infrastructure team, project leads, 3rd party vendors as needed, and key executive stakeholders.
- Annual Reports – The purpose of the annual report is to review objectives and discuss new initiatives. The annual report can also be used to illustrate trending for the past year and establish new goals for the upcoming year.
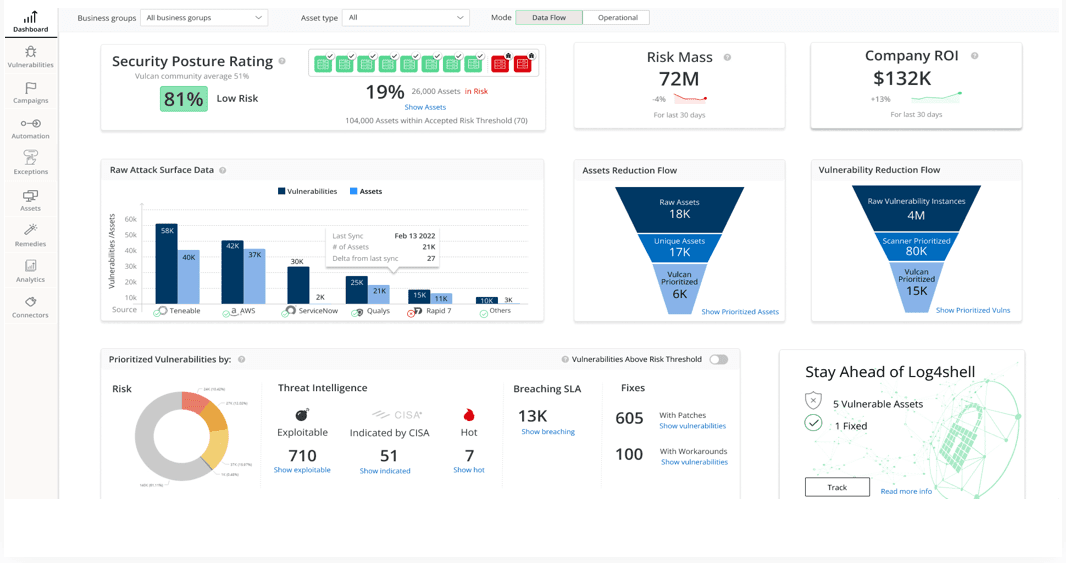
Dashboard Reporting
Dashboard reporting provides a real or point in time view of metrics that can supplement your existing reports.
Dashboards allows you to control access to who and what metrics your audience can view.
You can create an executive dashboard for managers or a general view for infrastructure teams or business units for up-to-date statistics.
Dashboards generally provide an export feature which allows the generation of instant reports.
3 Things People Forget When Reporting On Vulnerabilities
As discussed so far, there are a lot of moving pieces to include in an effective report.
Let’s take a look at a few items that should be included in the report and not left out.
Timelines
Establishing SLA’s is critical in reducing risk. The longer a system remains unpatched due to a zero day or critical severity, the odds of an exploit increase exponentially.
Measuring and recording remediation metrics is important and should definitely be included in the vulnerability report.
Completed Work
Ensure the report illustrates the ratio of open to closed remediated vulnerabilities.
Tracking closed incidents will help determine if additional resources are needed.
Ensure infrastructure and security teams that participate in the testing and patch management process are commended for their efforts and recognized for their contributions.
Currently Accepted Risk
Document exceptions or accepted risk by the business owners. This lets you track the risk appetite of your organization.
A high number of accepted risks may indicate an issue with policy SLA’s.
High trending over time for accepted risks should trigger a review of your risk acceptance policies.
How PurpleSec Supercharges Your
Vulnerability Reporting
PurpleSec’s Vulnerability Management platform can help you deliver and customize reports that measure the state of your vulnerability program.
Let’s examine the key components of the reporting engine that will supercharge and enhance the value of your vulnerability management program.
Matures Your Cyber Security Program
Enhances your security posture by providing key metrics that can help you quickly identify and assess risk in your organization.
Enables your support teams to work towards implementing a security framework or satisfy compliance requirements.
Helps your organization classify key business assets and provide guidance on where to prioritize remediation efforts.
Rapid Time To Value Solution
Obtain a quick return on security investment (ROSI) with PurpleSec’s vulnerability automation platform.
Shorten the attack vector by reducing the mean time to respond (MTTR).
Flexible And Customizable
PurpleSec’s Vulnerability platform can help you personalize your organization’s SLAs based on measured risk metrics and trends.
Integrate your existing tools seamlessly with PurpleSec’s platform to take advantage of its automation and agile detection algorithms.
Provides continuous and on-demand vulnerability remediation per your organization’s vulnerability management policy.
Wrapping Up
Vulnerability management reporting is a critical component of the vulnerability management process.
In this article, we have reviewed the benefits of continuous vulnerability reporting and the metric types that should be included within the report.
We also discussed how to present the vulnerability report to executive management and the importance of prioritizing assets to create risk scores for your most critical assets.
Finally, we highlighted features of PurpleSec’s automated Vulnerability Management platform and the value it provides for organizations interested in supercharging their vulnerability management reporting.
If you would like to learn more about the reporting platform or PurpleSec’s approach to Vulnerability Management, schedule a demo today to speak with a security expert.

Michael Swanagan, CISSP, CISA, CISM
Michael is an IT security expert with 15 years of proven experience. He has experience leading and supporting security projects and initiatives in the healthcare, finance, and advertising industry.
Recent Articles
Categories
Policy Templates
Most Popular