Credentialed scanning, using privileged credentials, provides in-depth vulnerability analysis and accurate results, assessing systems and apps not usually accessible without authentication. Uncredentialed scanning, without privileged credentials, is less accurate but can still reveal exploitable basic vulnerabilities.
Free Security Policy Templates
Get a step ahead of your cybersecurity goals with our comprehensive templates.
In today’s world of increasing cyber threats and data breaches, it’s more important than ever to ensure the security of your network and systems.
According to a recent study, the average cost of a data breach has been reported to be $4.45M in 2023, up 15% in the previous 3 years.
To make sure your organization does not become another victim, it’s critical to have the right security in place to make informed decisions and safeguard your organization’s sensitive information.
One of the crucial steps in achieving this security is conducting regular scans of your systems to identify vulnerabilities and potential risks.
However, choosing between a credentialed and an uncredentialed scan can be a difficult decision for many organizations.
This is because each type of scan has its own advantages and disadvantages that can impact the effectiveness of the scan and the security of the systems being scanned.
In this article, we’ll dive into the differences between credentialed and uncredentialed scans and help you understand which type of scan is best for your organization.
What Is The Difference Between Credentialed Scanning And Uncredentialed Scanning?
Vulnerability scans are a point-in-time assessment of computer systems or applications that identify potential security weaknesses.
Scanning your systems regularly helps to prevent cyber attacks and data breaches.
- Credentialed scanning involves the use of privileged credentials to scan systems and applications. This type of scanning provides an in-depth and comprehensive analysis of vulnerabilities and provides more accurate results.
- Uncredentialed scanning is conducted without the use of privileged credentials. This type of scanning is limited in its scope and provides less accurate results compared to credentialed scanning. Despite its limitations, uncredentialed scanning is still useful for identifying basic vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
Scanning for vulnerabilities is just one part of a comprehensive vulnerability management program.
Organizations must also take steps to mitigate and remediate identified vulnerabilities, and to continuously monitor their systems and applications for new vulnerabilities.
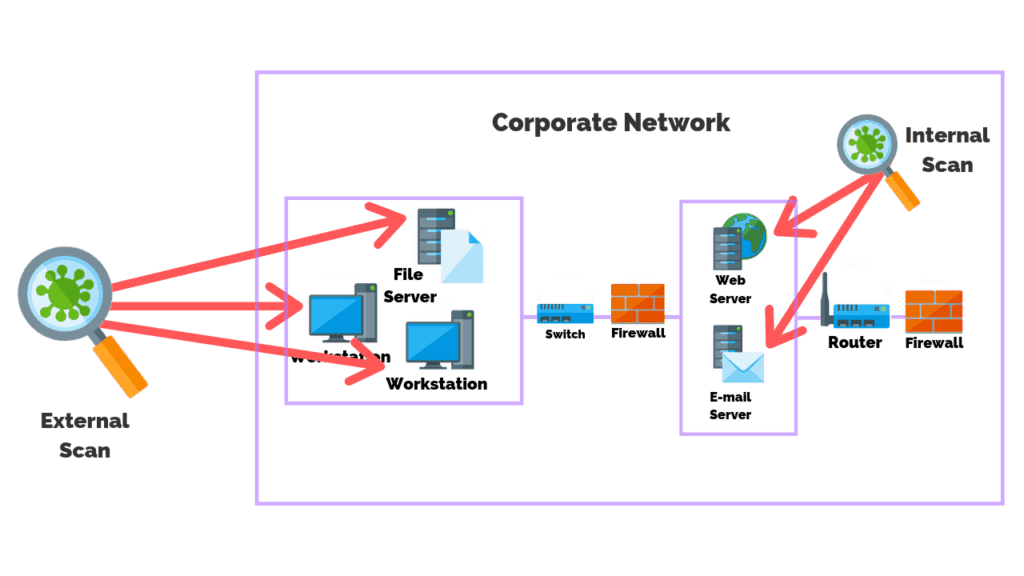
Internal VS External Vulnerability Scans
Internal and external vulnerability scans are two different types of scans that serve different purposes.
Internal scans are performed within an organization’s internal network, while external scans are performed from outside the network.
Likewise, internal scans are designed to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by internal actors.
External scans are designed to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by external actors.
Intrusive And Non-Intrusive Scans
Intrusive and non-intrusive scans are two different types of scans that are defined by their level of interaction with the system or application being scanned.
Intrusive scans actively test the system and application by sending requests, while non-intrusive scans only passively gather information about the system and application.
Environmental Scans
Environmental scans are scans that focus on a specific environment, such as a single network, application, or operating system.
Environmental scans provide a more targeted assessment of vulnerabilities and are useful for organizations that have specific security concerns.
It’s important to note, that credentialed and uncredentialed scanning can occur within internal, external, and environmental scans.
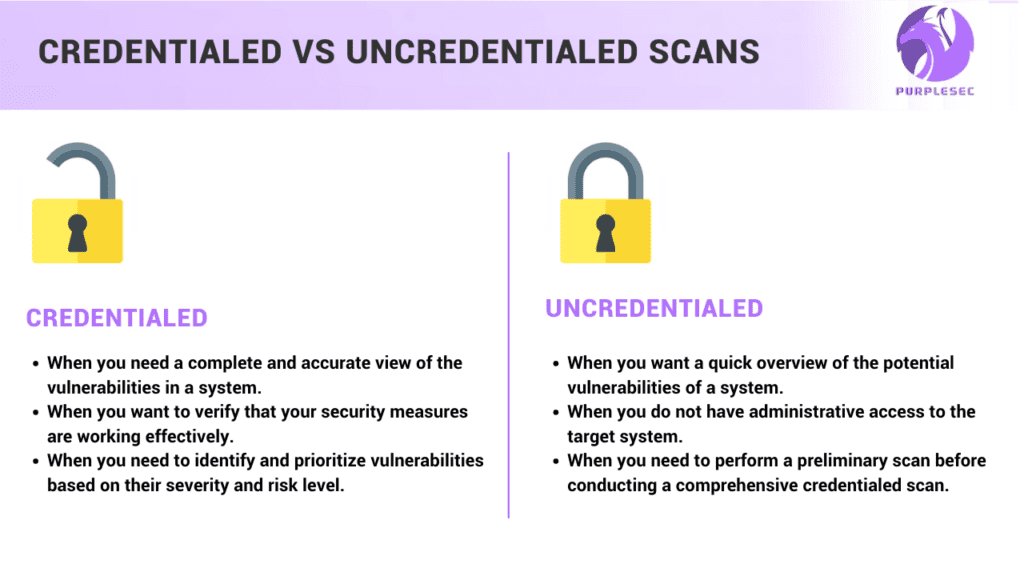
When Do I Need A Credentialed Or Uncredentialed Scan?
Credentialed scans are ideal for use in the following scenarios:
- When you need a complete and accurate view of the vulnerabilities in a system.
- When you want to verify that your security measures are working effectively.
- When you need to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and risk level.
Uncredentialed scans are ideal for use in the following scenarios:
- When you want a quick overview of the potential vulnerabilities of a system.
- When you do not have administrative access to the target system.
- When you need to perform a preliminary scan before conducting a comprehensive credentialed scan.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to conduct a credentialed or uncredentialed scan will depend on the specific needs and requirements of your organization.
Both types of scans have their own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to carefully consider your options before deciding on the best course of action for your security needs.
How Credentialed Scans Work
 Credentialed scans require administrative access to the systems being scanned and are performed using the same credentials and privileges as an administrative user.
Credentialed scans require administrative access to the systems being scanned and are performed using the same credentials and privileges as an administrative user.
The scans perform a thorough examination of the system, looking for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by a malicious attacker.
The power of credentialed scans is that they can provide a more accurate representation of a system’s security posture, as they can examine areas of the system that would otherwise be inaccessible to an uncredentialed scan.
In terms of environment, credentialed scans can be performed on both internal and external systems, making them typically more comprehensive than uncredentialed scans.
This is because credentialed scans take into account the specific configuration of each system, including installed software, hardware, and network topology.
The results are used to prioritize remediation efforts, as the vulnerabilities found are more likely to be real and exploitable.
Benefits Of Credentialed Scans
Credentialed scans offer several benefits compared to uncredentialed scans.
Some of the key advantages of credentialed scans include:
- More accurate results: Because credentialed scans have access to the inner workings of a system or application, they can provide more comprehensive and accurate results than uncredentialed scans.
- Ability to access sensitive areas: Credentialed scans have the ability to access sensitive areas of a system or application that would otherwise be off-limits to an uncredentialed scan.
- Ability to scan for privileged user vulnerabilities: Credentialed scans can help identify vulnerabilities that can only be exploited by users with elevated privileges. This is especially important for organizations looking to secure their systems and applications from attacks by malicious insiders.
- Better detection of misconfigurations: Because credentialed scans have access to configuration files and settings, they can provide a more complete and accurate assessment of a system’s configuration, including the detection of misconfigurations that could leave the system vulnerable to attack.
- Ability to scan for vulnerabilities in complex systems: Credentialed scans are better equipped to handle complex systems and applications with multiple dependencies and interrelated components.
Troubleshooting False Credentialed Scans
False positive results can occur in any type of vulnerability scan but are more common in credentialed scans due to the higher level of detail they provide.
You can get a false positive when the scanning software misinterprets the configuration of the system being scanned.
Or, when the software is unable to correctly identify the presence of a patch or update that has been applied to the system.
In order to minimize the occurrence of false positives, it is important to keep the scanning software up-to-date and to thoroughly test and validate the configuration of the system being scanned prior to the scan.
In addition, a careful review of the results of each scan should be performed to identify and eliminate any false positive results.
By taking these steps, organizations can ensure that their vulnerability management program is accurate and effective.
Windows Credentialed Scan Requirements
Credentialed scanning requires authentication to the target systems to perform a more in-depth scan of the environment.
When it comes to Windows environments, several popular tools can be used for credentialed scanning, including:
- Nessus – To get Nessus up and running for Windows environments, you’ll need a Windows administrator account with administrator-level privileges on the target systems. You’ll also need to install the Nessus agent on each system that you want to scan. The agent will report back to the Nessus server and provide information about the target system, including vulnerabilities, patches, and configurations.
- Rapid7 – Rapid7 offers a credentialed scanning solution that requires a Windows administrator account and the installation of the Rapid7 agent on the target systems. Once installed, the agent will report back to the Rapid7 server, providing information about the target system and allowing for a more in-depth scan.
- Qualys – Qualys is a cloud-based solution that requires a Windows administrator account and the installation of the Qualys agent on the target systems. Qualys also offers the ability to perform scans from a cloud-based perspective, providing a unique view of the target environment.
Credentialed Scans For Linux Environments
Depending on the vulnerability scanner you choose a Linux environment, similar to a Windows environment, requires you to install the necessary packages and plugins, configure authentication, and a clearly defined scope of the scan.
The main difference is that Linux systems have their own unique set of vulnerabilities and security configurations.
It is recommended that you perform credentialed scans for Linux environments to get a deeper and more thorough assessment of the system.
By having access to the underlying system and its configurations, the scan can provide a much more accurate picture of the vulnerabilities and risks present.
This information can be used to implement appropriate security measures and improve the overall security posture of the system.
Credentialed Scans For Applications
This type of scan requires access to the application’s source code, databases, and configuration files to provide a comprehensive view of the application’s security posture.
Tools like BurpSuite or Zap can be used to conduct credentialed scans for applications.
These scans are especially useful for identifying vulnerabilities in custom-built applications, which can often have security flaws that go unnoticed.
How Uncredentialed Scans Work
Uncredentialed scans work differently from credentialed scans, as they do not require access to the target system’s credentials.
Instead, they rely on network-level information and publicly accessible information to identify vulnerabilities.
The process of an uncredentialed scan involves identifying the target systems and applications and then probing them for known vulnerabilities.
Next, the scan then generates a report highlighting any potential security risks and weaknesses.
Best practices for conducting uncredentialed scans include:
- Regularly scanning the environment.
- Updating the scan engine regularly to ensure that it can detect the latest vulnerabilities.
- Performing scans in a controlled environment to minimize any potential disruption to the target system.
It’s important to have a clear understanding of the target system and its intended use, as well as any relevant regulations, to ensure that the scan is conducted in a compliant manner.
Benefits Of Uncredentialed Scans
Uncredentialed scans can be run on any system, regardless of whether the scanner has access to the credentials or not.
This allows for quick and easy assessments of systems that may not have the necessary authentication to allow for a credentialed scan.
Uncredentialed scans can often provide a high level of detail about the vulnerabilities present on a system, as the scanner does not have to rely on the accuracy of the information provided by the system itself.
This can be particularly useful in cases where a system may have been configured in such a way as to hide certain vulnerabilities or provide false information about its security status.
Uncredentialed scans are often much quicker and less resource-intensive than credentialed scans.
This is because the scanner does not have to spend time attempting to authenticate with the system or interacting with it in any other way.
Instead, the scan can simply be run, and the results analyzed, making it ideal for large-scale assessments or for quickly identifying any critical vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
Uncredentialed scans can also be a useful way to identify the overall security posture of a network.
By assessing the security of systems and applications from an external perspective, it is possible to gain a clear picture of the strengths and weaknesses of the network.
This can help organizations to prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources more effectively.
How PurpleSec Is Improving Vulnerability Scanning
PurpleSec’s vulnerability management services offer a comprehensive solution to organizations struggling with the complexity and resource constraints of their vulnerability scans.
Case Study: How We Reduced Vulnerability Risk By 86%
Our managed vulnerability management platform provides the benefits of both credentialed and uncredentialed scans, and our team of experts is always available to help you make the best decision for your security needs.
We use automation to streamline the process and provide you with a single view of your security risk.
By partnering with PurpleSec, you can take your security to the next level, without adding more resources to your team.
Our team of experts will monitor your systems 24/7, and provide you with real-time insights and recommendations to help you improve your security posture.
The program includes regular scans, vulnerability assessments, and remediation support, ensuring organizations stay ahead of potential threats and maintain a secure environment.
This results in an efficient and cost-effective solution, increasing the accuracy and efficiency of processes.
Wrapping Up
Vulnerability scanning is a crucial part of any comprehensive security strategy and understanding the benefits of both uncredentialed and credentialed scans is key to effective vulnerability management.
While uncredentialed scans are quick and easy to perform and can provide high-level insights into the overall security posture of a network, credentialed scans offer a more comprehensive view of vulnerabilities and are better suited for verifying the effectiveness of security measures.
Ultimately, the choice of which type of scan to perform will depend on your specific security needs and goals.
So don’t be a vulnerability victim – scan your systems today!
Let’s schedule a demo so you can see how our platform works and understand the value it can bring to your organization
Article by