How To Prevent A Buffer Overflow Attack
A buffer overflow is one of the best known forms of software security vulnerability and is still a commonly used cyber attack.
You can prevent a buffer overflow attack by auditing code, providing training, using compiler tools, using safe functions, patching web and application servers, and scanning applications.
Learn More: How To Prevent Cyber Attacks
Free Security Policy Templates
Get a step ahead of your cybersecurity goals with our comprehensive templates.
What Is A Buffer Overflow Attack?
In a buffer overflow attack, an application receives more input than it expects. As a result, the error exposes the system memory to a malicious threat.
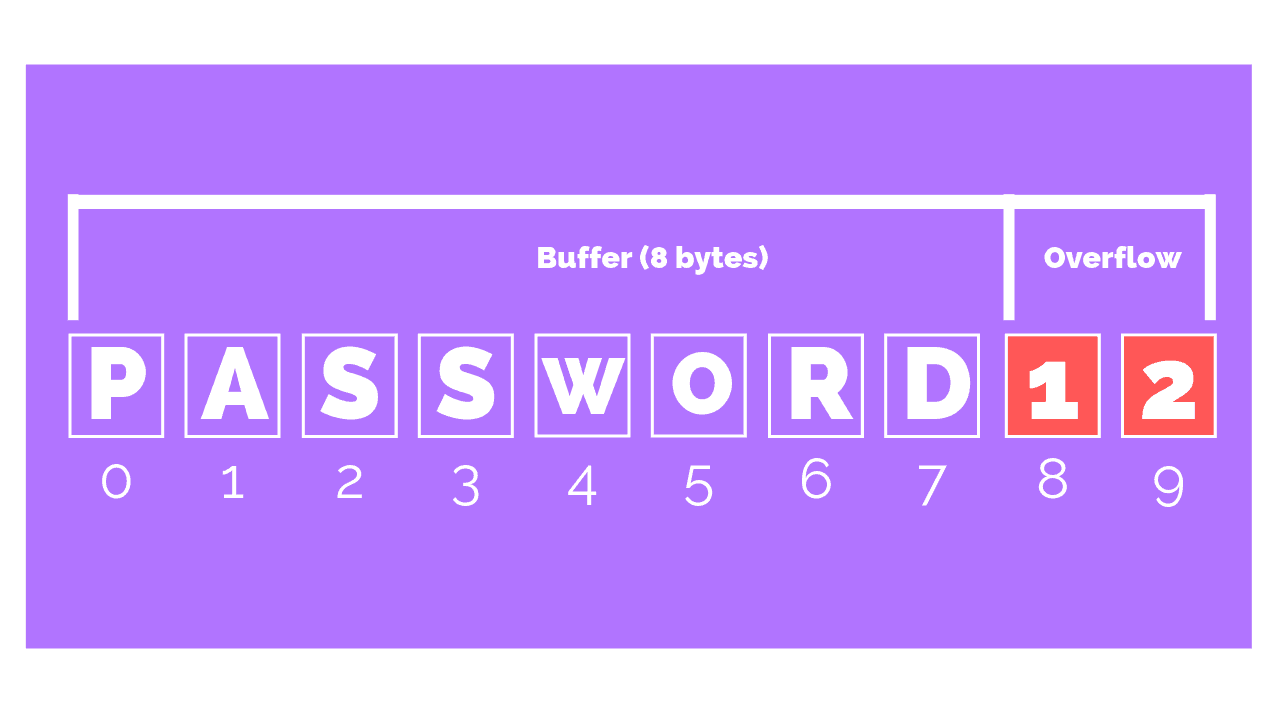
While a buffer overflow itself doesn’t cause damage, it does expose a vulnerability.
Threat actors are then able to access memory locations beyond the application’s buffer, which enables them to write malicious code into this area of memory.
When the application is executed the malicious code is launched.
Example Of A Buffer Overflow Attack
In 2014, a buffer overflow vulnerability in the OpenSSL cryptography library was disclosed to the public.
This flaw, known as the Heartbleed bug, exposed hundreds of millions of users of popular online services and software platforms to a vulnerable version of the OpenSSL software.
The Heartbleed bug serves as a reminder of the importance of regular patching and staying aware of bug reports.
Free Security Policy Templates
Get a step ahead of your cybersecurity goals with our comprehensive templates.

How Do You Prevent A Buffer Overflow Attack?
Routine Code Auditing
This can be done both manually and automatically. Manual code auditing involves developers reviewing their code to identify potential vulnerabilities. Automated code auditing can be performed using static analysis tools that scan the code for common security vulnerabilities.
Training
Developers should be trained on secure coding practices, including bounds checking, avoiding the use of unsafe functions, and adhering to group standards. This training can help developers write code that is less likely to have buffer overflow vulnerabilities.
Compiler Tools
Tools like StackShield, StackGuard, and Libsafe can add a layer of protection against buffer overflow attacks by detecting and preventing stack overflows.
Safe Functions
Using safe functions such as strncat instead of strcat, strncpy instead of strcpy, etc., can help prevent buffer overflow attacks. These functions include bounds checking to ensure that data does not exceed the buffer size.
Regular Patching
Regularly patching web and application servers and staying aware of bug reports relating to applications upon which your code is dependent can help prevent buffer overflow attacks.
Learn More: How To Automate Your Patch Management
This is because patches often fix known vulnerabilities that could be exploited through a buffer overflow attack.
Scanning Applications
Periodically scanning your application with one or more of the commonly available scanners that look for buffer overflow flaws in your server products and your custom web applications can help identify potential vulnerabilities.
These scanners can provide detailed reports on potential security issues and suggest ways to fix them.
Article by