Previous

Google SEO Poisoning Campaign Compromises 15,000 Sites
Learn how PurpleSec’s experts can protect your business against the latest cyber attacks.
Author: Eva Georgieva / Last Updated: 12/16/2022
Reviewed By: Dalibor Gašić, & Michael Swanagan, CISSP, CISA, CISM
View Our: Editorial Process
Table Of Contents
Summary Of The Attack
- Around 15,000 sites were compromised in a major search engine optimization campaign.
- The victims were redirected to fake Q&A discussion forums.
- WordPress PHP files of the websites were modified and injected to increase malicious sites rankings.
- The attack was first spotted by Sucuru.
- The threat actors probably tried to conduct an ad fraud.
What Is SEO Poisoning?
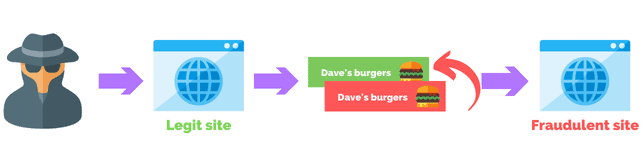
SEO poisoning is a type of cyber attack where a threat actor attempts to manipulate search engines into ranking compromised websites higher in search results.
This can be done by using keywords related to popular search terms, creating fake backlinks, or injecting malicious code into legitimate websites. When a user visits the compromised site they may be redirected to a phishing site that hosts malware, or a site that displays unwanted or inappropriate content.
Why Are Threat Actors Using Google Search?
The reason behind why URLs selectable from Google Search are used is because the URL performance metrics are increased. This is important for the page to be indexed by the platform leading to greater visibility and more visitors to the site.
Also in this manner, some security controls are bypassed and the traffic is classified as legitimate.
Another thing used is the exclusion of logged in users as well as those entering through wp-login.php, which aims to avoid the redirection of an administrator of the site which would raise suspicion and possible alerting and cleaning of the compromised site.
The Anatomy Of The Attack
Attackers modified WordPress PHP files of the websites, some of them being ‘wp-singup.php’, ‘wp-cron.php’, ‘wp-settings.php’, ‘wp-mail.php’, and ‘wp-blog-header.php’, with the goal to inject the redirects to the fakes Q&A discussion forums. The final goal is to increase the rankings of fake sites in search engines.
First Signs Of The Attack
The attacks were spotted primarily by Sucuri and the analysis says that each compromised site that is used as part of the scheme contains approximately 20,000 files used as part of the search engine spam campaign, with most of the sites being WordPress.
What the researchers have also noticed is the presence of ads.txt files on the landing pages which could also indicate that the threat actors are trying to increase traffic to their fake sites in order to commit ad fraud.
What Is Ad Fraud?
Adware, or also known as advertising-supported software, are usually used to make revenue for its developers by automatically generating advertisements on the user’s screen. The ads can usually be found within a web browser.
Money can be made from adware from the following methods:
- Pay-per-click – With this method developers get paid each time the user opens an ad.
- Pay-per-view – Money is generated each time the user is shown an ad.
- Pay-per-install – Revenue is made each time bundled software is installed on a device.
Ad fraud, specifically, is any attempt to defraud digital advertising networks for financial gain.
Scammers often use bots to carry out these types of frauds, but that might not always be the case. There are a variety of ways cybercriminals can carry out ad frauds.
Some of these are hidden ads, when an ad is shown in such a way that the user doesn’t actually see it. This kind of fraud targets ad networks that pay based on impressions, which are views, not clicks.
How The Attack Happened
Besides infecting some of the files, the attackers also injected a few of them by changing just slightly the name of the aforementioned files so they look like legitimate ones.
Those, whether injected or infected files contain malicious pieces of code that then check if the website visitors logged into WordPress, and if not, redirects them to https://ois.is/images/logo-6.png URL.
What happens after that is that an image is not loaded, as the user expects but instead JavaScript is loaded that redirects the users to a Google Search click URL that redirects the users to a promoted Q&A site.
The image file uses the ‘windows.location.href’ function and redirects the user to one of the following domains:
- qa.istisharaat[.]com
- en.photolovegirl[.]com
- en.poxnel[.]com
- Qa.tadalafilhot[.]com
- Questions.rawafedpor[.]com
- qa.elbwaba[.]com
How Site Owners Can Prevent This Attack
The recommendation is to upgrade all WordPress plugins and website CMS to their latest version and to activate 2 Factor Authentication (2FA) on all admin accounts.
Related Articles

Eva Georgieva
Eva is a security engineer, researcher, and penetration tester with over 5 years of experience working on both red teams and blue teams.
Recent Attacks
- Top 10 Cyber Attacks In 2022
- Top 10 Vulnerabilities In 2022
- Rackspace Ransomware Attack
- Dropbox Suffers Data Breach
- Iranian APT Uses Log4j
- Google SEO Poisoning Campaign
- Killnet DDoS Target Airports
- Advocate Aurora Health Data Leak
- Microsoft 2.4 TB Data Leak
- Optus Exposes 2.1M Customers
- $570M Binance Coin Hack
- TikTok Denies Cyber Attack
- NATO Data Leak
- Uber’s Systems Compromised
- Cisco Cyber Attack
- Samsung Exposes PII
Popular Articles
Ransomware Attacks
Preventing Attacks





 HEALTHCARE
HEALTHCARE GOVERNMENT
GOVERNMENT CRYPTO
CRYPTO